- ....1.1
- Quantities such as
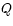 and
and 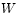 are
often called process variables.
are
often called process variables.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... space''.2.1
- The term is
probably due to Paul Ehrenfest who in his classical book
on Statistical Mechanics refers to
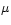 -space, or ``molecular'' space as opposed to
-space, or ``molecular'' space as opposed to 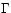 , or ``gas'' space (see
Chapter 3 below).
, or ``gas'' space (see
Chapter 3 below).
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...
reads3.1
- In an MD simulation not only the total energy but
also the total momentum
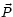 is conserved; this should be kept
in mind when comparing simulation results to theoretical statements.
Actually, the four conditions
is conserved; this should be kept
in mind when comparing simulation results to theoretical statements.
Actually, the four conditions
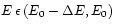 and
and 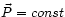 , would define a
, would define a 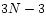 -dimensional
spherical shell in velocity space. However, for sufficiently numerous
particles (
-dimensional
spherical shell in velocity space. However, for sufficiently numerous
particles (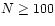 ) this detail may be neglected, and we can
base the argumentation just on the condition
) this detail may be neglected, and we can
base the argumentation just on the condition
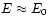 (with a
(with a 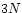 -dimensional shell).
-dimensional shell).
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... size3.2
- A particularly powerful formulation of classical
mechanics, known as Hamilton's formalism, makes use of
the variables
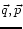 (position and momentum)
in place of
(position and momentum)
in place of
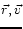 (position and velocity.)
In this notation the phase space cells have the size
(position and velocity.)
In this notation the phase space cells have the size
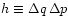 .
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.